Throughout history, the concept of childhood has been defined from various perspectives by scientists, philosophers, religious figures, state leaders, educators, and anyone involved with children, varying across societies and cultures. However, during the Middle Ages, childhood was not recognized as a distinct period; rather, children were seen as miniature adults and integrated into adult life as soon as they were out of infancy. In fact, after the age of 0-2, they were dressed like adults and considered a part of adult society. It was only in 1948 that childhood was legally defined in the United Nations Declaration of the Rights of the Child as the period from birth to 18 years of age.
In the 21st century, we now understand that children are not miniature adults but individuals with unique cognitive, mental, and physical developmental needs at different stages. Likewise, it is widely accepted in all medical fields that children's medical needs differ from those of adults and should be addressed by specialists trained in pediatric care.
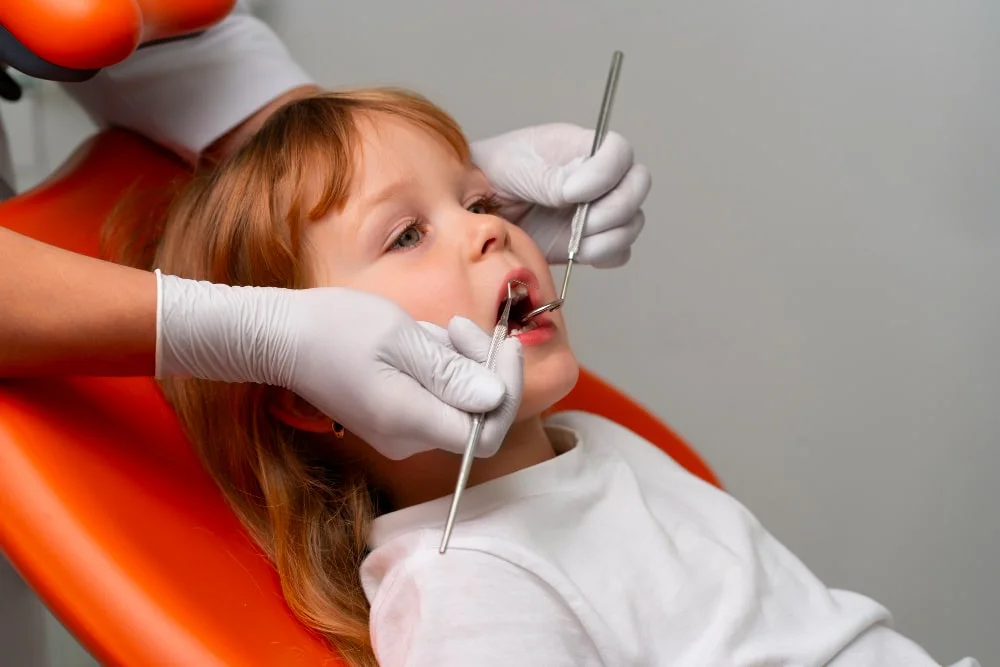
Pediatric dentistry (Pedodontics) is a specialty awarded to dentists who, after completing their basic dental education, undergo specialized training or a doctoral program in the Department of Pedodontics at dental faculties. During their training, pediatric dentists not only learn treatment principles based on the child’s developmental stages but also receive education on the medical and psychological aspects of childhood development. They are trained in behavior management techniques to prevent dental fear in children, assess the risk of dental caries, develop personalized preventive programs, plan caries-preventive dietary recommendations, implement treatment approaches suitable for the dental and jaw development of children, and perform treatments under general anesthesia or sedation with minimal risk of complications. Additionally, they are trained to manage dental trauma in the jaw and facial region, as well as preventive and early orthodontic treatments for anomalies caused by developmental issues or harmful habits. Moreover, pediatric dentists possess the necessary expertise to provide dental care not only to medically healthy children but also to children with disabilities and special needs.
Pediatric dental treatments cover children and young adults aged 0-18. Therefore, when choosing a dentist for this age group, it is essential to seek out a specialist in pediatric dentistry. In our country, dental specialties are not widely known among the public, and due to this lack of awareness or financial constraints, families often choose general dentists instead of specialists.
To ensure the early detection of developmental or acquired dental and jaw diseases in children and to educate families on how to maintain their child's oral and jaw health, children should visit a pediatric dentist between 6 months and 1 year of age, even if they have no complaints. Regular follow-ups as advised by the specialist are crucial to maintaining oral health and assessing risk factors. It should be remembered that the most cost-effective and healthiest treatment approach is preventive care before any pain or problems arise. Worldwide, dental caries are the first painful health issue encountered by children. Therefore, introducing children to the dentist before they experience pain can help prevent them from having early negative pain experiences.
Prof. Dr. Ayça Tuba ULUSOY
Pediatric Dentist